- Our Services
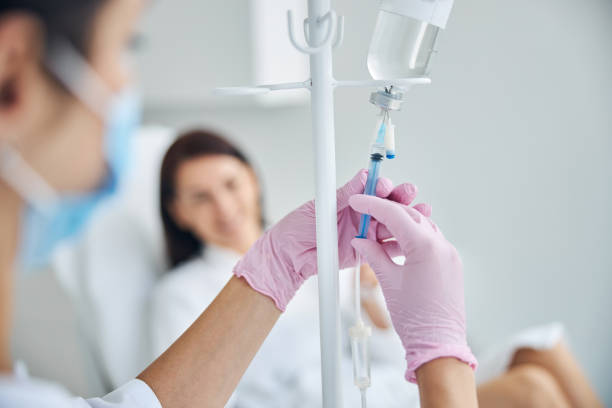
IV,IM Injection
An Injection is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle and a syringe. An Injection is considered a form of parenteral drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous, intramuscular (IM), and intravenous (IV) injections, as well as less common injections such as intraperitoneal, intraosseous, intracardiac, intraarticular, and intracavernous injections.
The term Injection is sometimes used synonymously with inoculation, but injection does not only refer to the act of inoculation. Injections generally administer a medication as a bolus (or one-time) dose, but can also be used for continuous drug administration. After Injection, a medication may be designed to be released slowly, called a depot injection, which can produce long-lasting effects.
An Injection necessarily causes a small puncture wound to the body, and thus may cause localized pain or infection. The occurrence of these side effects varies based on injection location, the substance injected, needle gauge, procedure, and individual sensitivity. To prevent the localized pain that occurs with injections the injection site may be numbed or cooled before injection and the person receiving the injection may be distracted by a conversation or similar means. To reduce the risk of infection from injections, proper aseptic technique should be followed to clean the injection site before administration.
Tag Man Power offers professional IV IM injection services in Chennai. Our skilled healthcare professionals provide safe and effective medical injections at home.